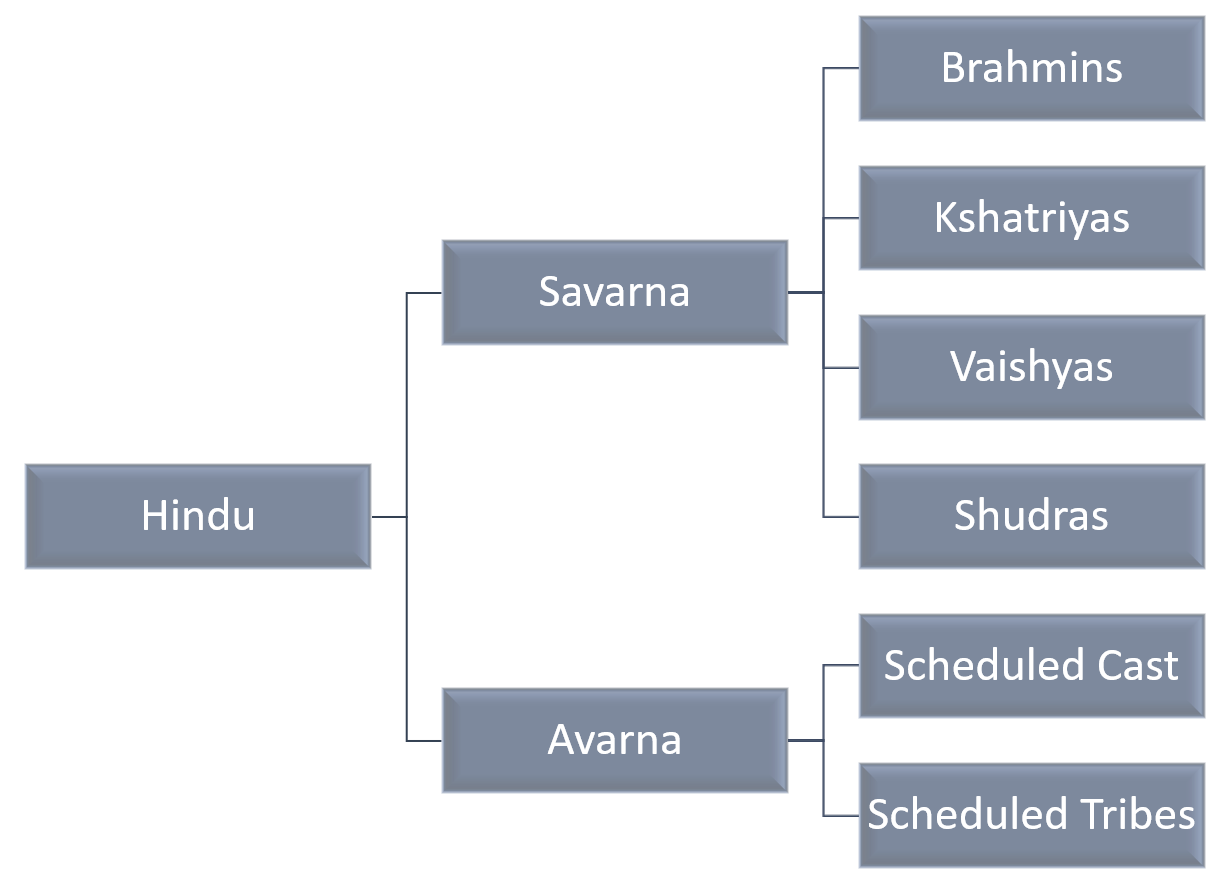
The Savarna and Asavarna are part of the caste system of Hindus. Those communities that belong to one of four Varana as per their fit are called Savarna Hindu but there are many more people and communities which are not part of any Varnas like Tribes and Dalits they were put in another category called Avarnas.
The evolution of the Lower caste to modern-day Scheduled Castes is complex. The caste system as a stratification of classes in India originated about 2,000 years ago and has been influenced by dynasties and ruling elites. The Hindu concept of Varna historically incorporated occupation-based communities.
The Dharmashastras
The Varnas system is extensively described in the Dharmashastras. This Varna is divided into four Varnas (Brahmins, Kshatriya, Vaishya and Sudras). Those who fall out of this system because of their grievous sins become outcastes (untouchables) and considered outside of the Varna system. Those who are unrighteous or unethical are also considered outcasts.
Dalit
The term Dalit is a self-applied concept for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste hierarchy. According to Economist and reformer, Dr BR Ambedkar untouchability came into Indian society around 400 CE, due to the struggle for supremacy between Buddhism and Brahmanism (an ancient term for Brahmanical Hinduism). Some Hindu priests befriended untouchables and were demoted to low-caste ranks.
In the late 1880s, the Marathi word 'Dalit' was used by Mahatma Jotiba Phule for the outcasts and Untouchables who were oppressed and broken in the Hindu society.
Adivasi is the collective term for the Tribes of the Indians. who are considered to be the indigenous people of India.
Some scholars and professors have suggested the lack of resemblance between India's ancient and modern era caste systems in India.
Patrik Olivelle, a professor of Sanskrit and Indian Religions and credited with modern translations of Vedic literature. States that the Dharma-Sutra and Dharma-Shastra in ancient and medieval Indian texts do not support ritual pollution, purity-impurity as the basis of the Varna system, but in the context of individual's moral, rituals and biological pollution (like eating meets). Massive focus on matters relating to purity/impurity in the Varna. Whereas all four Varnas could carry purity/impurity by the content of their character, ethical intent, actions, innocence or ignorance, stipulations, and ritualistic behaviours.
" in ancient and medieval Indian texts do not support ritual pollution, purity-impurity as the basis of Varna system "
The first three Varnas are described in the Dharmashastras as "twice-born" and they were allowed to study the Vedas. Such restrictions were not found in Vedic-era literature.
" Restriction of who can study Vedas is not found in Vedic-era literature "
 |
| Irula men from the Nilgiri Hills in Tamil Nadu, c.1871 |
Each community and society have there own culture and different mythologies and rituals, all have their own spiritual value as India is a country of different cultures, languages and traditions. Many people do not understand the language each other but all are Indians.